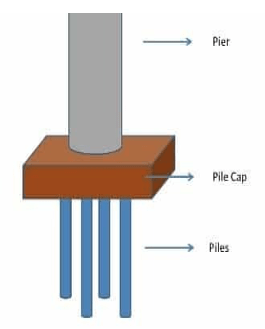
Pile foundations are deep foundations. They are formed by long, slender, columnar elements typically made from steel or reinforced concrete, or sometimes timber. A foundation is described as ‘piled’ when its depth is more than three times its breadth.
Pile foundations are principally used to transfer the loads from superstructures, through weak, compressible strata or water onto stronger, more compact, less compressible and stiffer soil or rock at depth, increasing the effective size of a foundation and resisting horizontal loads. They are typically used for large structures, and in situations where soil is not suitable to prevent excessive settlement.
Common uses
- As heavy foundations, securing deep excavation especially close to existing buildings as well as stabilising and retaining slopes
- In a variety of infrastructure projects such as tunnelling, road or bridge construction as well as flood protection
- Transfer to deep rock or competent soils and withstand high loads
- Retain ground alongside an excavation pit or close to adjacent buildings, often combined with other techniques such as ground anchors or soil nails
- For slope stabilisation to prevent landslides, or protect existing buildings
Advantages
- Can support high loads
- Various diameters available from 450mm upwards
- Minimal settlement and deformation
- Minimum vibration