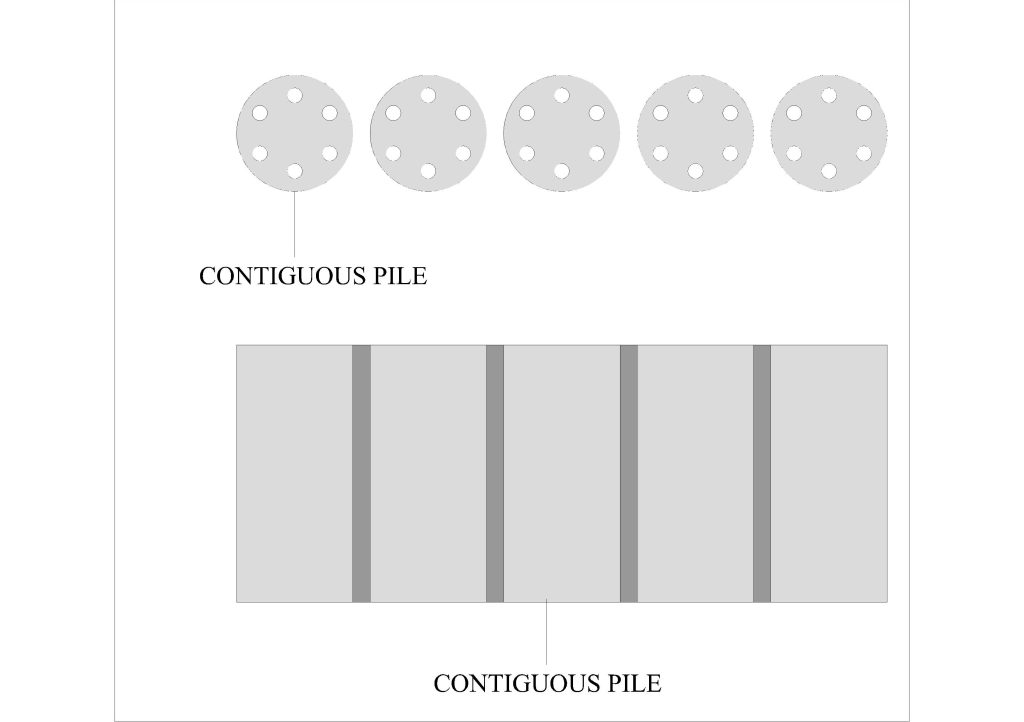
Series of adjacent piles constructed to form an earth retaining structure as a cantilever or a propped cantilever wall. Contiguous piled walls consist of a row of successive unconnected cast-in-situ concrete piles constructed with small gaps between the adjacent piles, formed using CFA or rotary bored piles (replacement piles techniques). Compared to other lateral soil supporting systems, contiguous pile walls are a more simple and economical supporting system due to reduction in cost and construction period when considering small to medium scale depths of excavations. The diameter of each pile in a contiguous piled wall is usually not less than 300mm diameter.
Contiguous piles are suitable where the groundwater table is below excavation level. It is normally the most economic and rapid option. The wall consists of discrete piles typically installed at centres 150mm greater than their diameter, leaving gaps where soil is exposed during excavation.
Common uses
- Support of excavations
- Slope stabilisation
- Support wing walls
Advantages
- Limited load from surrounding structures taken
- Allows easier work in open excavations when in cantilever
- New basement structures, especially in urban areas
- Additional support for highways subject to embankment slippage (slope stability)
- Bridge abutments carrying horizontal loads