Grouting is a process of ground improvement by injecting the cementing material, chemical to reduce the permeability of ground and increase shear strength. Cement-based grouts, ultrafine and chemical grouts are popular these days.
The common type of grouting techniques and their suitability’s:
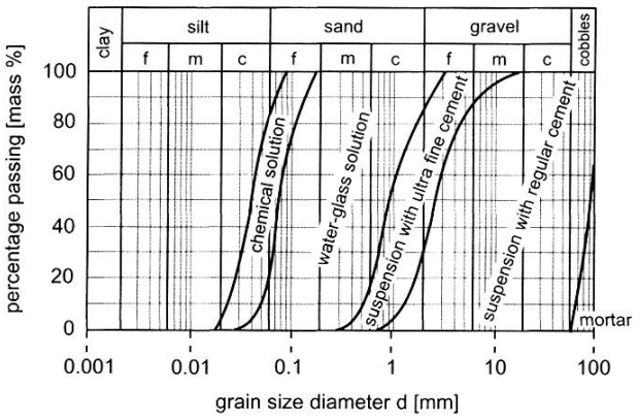
The following chart depicts the suitability of grout according to grain size diameter.
Grout Classification:
- Permeation grouting
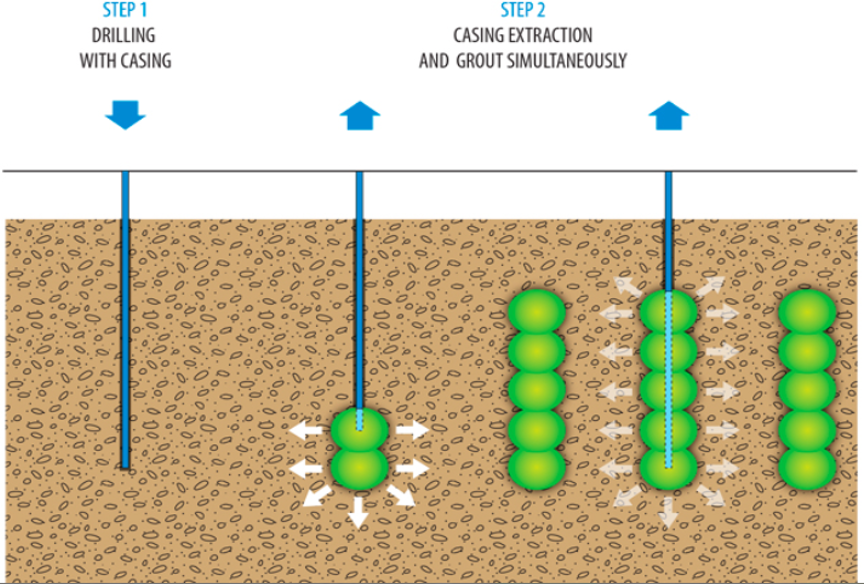
Permeation grouting is a low-pressure grouting method to fill voids and cracks in soils and rock. In permeation grouting, the grout flows and permeates through coarse granular soils, sandy soils. Due to the solidification of mass, the strength and stiffness of strata improve, and permeability reduces after permeation grouting. 
Suitability: This grouting technique is suitable for gravel, sandy soils, decomposed rock, and fissured rock. Features of permeation grouting are to provide protection by increasing the cohesion between particles while excavating to adjacent structures.
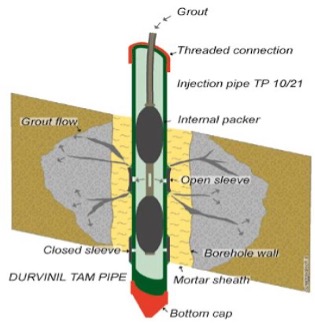
2. Tam grouting
TAM (Tube a Manchette) method of grouting involves an injection of grout under pressure through a perforated pipe along with a special sleeve grout into grout holes, soils, or disintegrated rocks. The pipes are inserted into the holes at closely spaced intervals with short sections of rubber sleeve (Manchette) on the outer part of the pipe that acts as a one-way valve.
Partial or complete displacement of infill water between soil particles occurs because of this technique; hence, reducing permeability and increasing strength. A double packer is used to pump the grout into the manchette tube until the packer is halfway past the set of the holes drilled into the tubes.
Suitability: This type of grout technique is effective for sealing mass above tunnel excavation, sealing mass behind pile wall, sealing mass while construction of cofferdam, strengthening loose soil mass.
3. Fracture grouting/ compensation grouting
This grouting is a process of injecting grout slurry of thick grout under high pressure. TAM pipes are used to create the fractures in the soil/ disintegrated strata, which are then filled with grout. The grout flowing the fractured path follows the plane of minor principle stress. Thus this method compensates for the settlements and is used to uplift the deformed structures.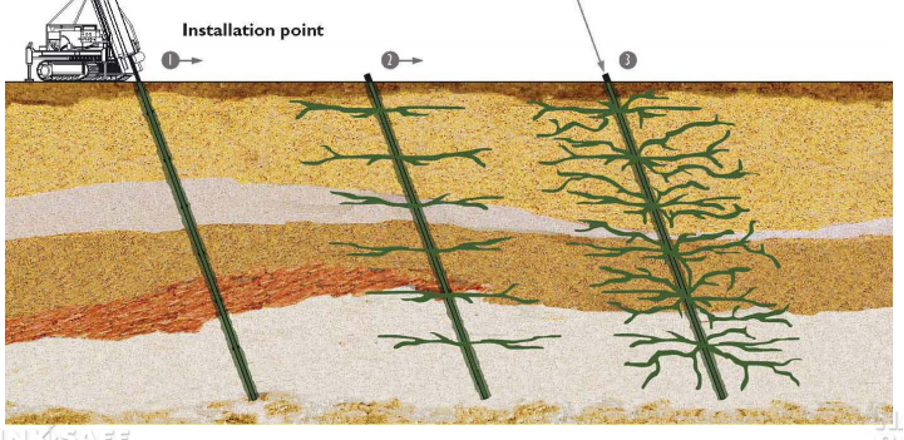
Source: 9th annual, Breakthroughs in tunneling- short course/ pdf.
Suitability: This technique is applicable mainly in the sand, silt, clay, decomposed rock, fissure rock, and fills with rock. It is suitable for void filling, restoration/ uplift the settling structure. This grouting will be ineffective in the gravel and voided groundmass conditions.
4. Compaction grouting
Compaction grouting is single-stage grouting that involves the injection of thick grout to create a bulb at the end of the pipe; this leads to densification of mass at the bottom of the pipe.
A high viscosity (low mobility/low slump typically 50 mm) aggregate grout is pumped into the ground in stages in primary, secondary, and tertiary locations to density the whole mass.
Source: siwssboring.com/ technologies/compaction grouting
Suitability: This grouting is suitable for almost all types of soil conditions. This method is applicable in the clay and silts for strengthening and increasing the bearing capacity. It leads to lateral densification of strata, lift the settled structures, remediation for karst, sinkholes.
5. Jet grouting
Jet Grouting is a high-pressure grouting technique that utilizes high-pressure cutting jets of cement, water, and air shrouding with high velocity (>100m/s).
High-speed cutting jets of water or cement (grout) the system erodes the strata and mix into in-situ soil mass to form a composite soil-cement solidified mass.
Source: pilebuck.com/soil improvement techniques.
Suitability: This grout technique gives more strength to soils; this is suitable for the clays, silts, sandy soils, and gravel but less use in boulder conditions. This grouting is not suitable for the fissured rock and void-filled mass condition but uses in the decomposed rock conditions. It is applicable for retaining the ground systems, cut-off barriers, underpinning.
Source of first picture: https://nptel.ac.in/content/storage2/courses/105108075/module6/Lecture20.pdf